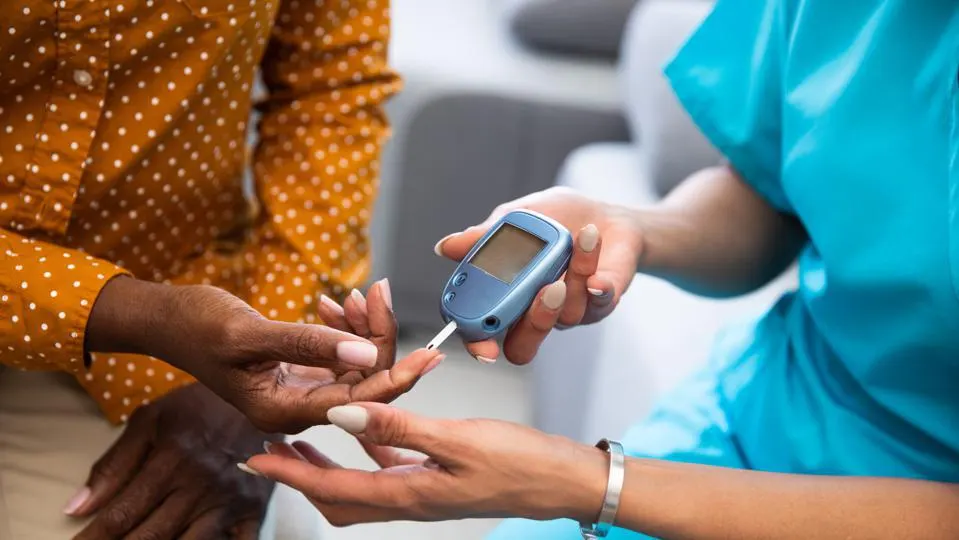
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition that affects the way your body metabolizes sugar (glucose). Unlike Type 1 diabetes, where the body doesn’t produce insulin, in Type 2 diabetes, the body either doesn’t produce enough insulin or the insulin it produces isn’t used effectively. This leads to high blood sugar levels.
Key Points About Type 2 Diabetes:
- Insulin Resistance: The primary problem in Type 2 diabetes is insulin resistance. Your cells don’t respond to insulin as well as they should, which means glucose stays in the bloodstream instead of being used for energy.
- Insulin Production: Over time, the pancreas may not be able to produce enough insulin to overcome the resistance, leading to elevated blood sugar levels.
- Symptoms: Common symptoms include frequent urination, excessive thirst, extreme fatigue, blurred vision, and slow-healing sores. Some people may not have noticeable symptoms, especially in the early stages.
- Risk Factors: Key risk factors include being overweight, having a sedentary lifestyle, a family history of diabetes, and older age. It is also more common in certain ethnic groups, such as African American, Hispanic, and Asian American populations.
- Management: Type 2 diabetes can often be managed with lifestyle changes such as a healthy diet, regular physical activity, and weight management. Medications and insulin may also be prescribed if lifestyle changes alone are not enough to keep blood sugar levels in check.
- Complications: If not managed properly, Type 2 diabetes can lead to serious health complications, including heart disease, nerve damage, kidney damage, eye problems, and increased risk of infections.
Managing Type 2 diabetes involves working closely with healthcare providers to monitor blood sugar levels, make necessary lifestyle adjustments, and possibly use medications to maintain optimal health.